A simple geometric picture in the model 4D-medium is applied to explain the effect of expansion of galaxies. It is shown that the formation of galaxies could occur as a result of the bombing of the Universe by the clots of the 4D-matter from a distant source. The velocity of galaxies defined by their deviation from the axial line passing through the center of the Universe to the source. Because of the sphericity of the Universe of this deviation depends on the angle of inclination of the vortex, which is formed upon impact bunch of matter on the Universe and then turns into a galaxy or a star. Also explains the reason for the formation of vast dark regions of the Universe, which does not show any stellar objects.
As it is known from astronomical observations the rate of recession of galaxies V is proportional to the distance r up to them and the coefficient of proportionality is the Hubble constant H:
V = H r (1)
In the framework of the 4D-medium [1] this fact can give the following interpretation.
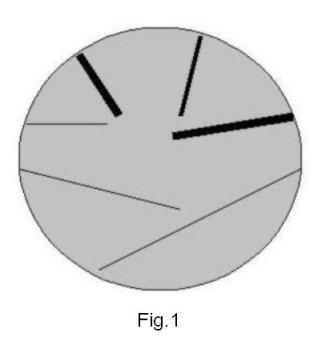
Let us imagine our Universe as a four-dimensional sphere, consisting of a certain matter, and galaxies and other stellar objects - in the form of vortices in the bulk of this matter, having access to three-dimensional surface of the ball, the four-dimensional sphere, which we call the visible World. In a rough approximation, these objects can be considered as one-dimensional straight lines, as shown in one section of the Universe in Fig. 1. It was established from an analysis of the Lorentz transformation [2], the motion of the vortex is provided due to its inclination relative to the normal, held to the hypersurface 4D-sphere. Then the velocity V is
V = c sin(α) (2)
where c is the speed of light, α is the angle of inclination.
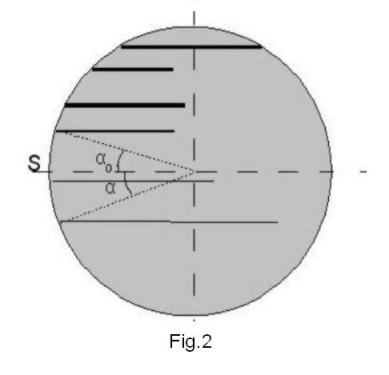
The mechanism of galaxy formation was proposed [3] and is bombarding our Universe by the clots of 4D-matter, which can be treated as other 4D-universes with smaller size and is expected to exist and be in motion in four-dimensional space. If the distribution of such clusters is uniform, then they would have to leave in a collision with our Universe stellar objects in it with a random distribution of velocities. Since it is not so, then we can assume that the source gave rise to galaxy clusters of matter, was at a considerable distance from our Universe. For example, such a source could be a collision of two sufficiently large universes, which could have happened billions of years ago rather far from our Universe. It then follows that these clots left in our Universe, would form bundle of almost parallel lines, as shown in Fig. 2. The angles of inclination of these lines to the surface of the sphere and hence the speed of galaxies are distributed evenly, depending on the distance from point S, is closest place in the Universe to the source. Suppose that our galaxy, the Milky Way, is located away from the points of S and its position on the surface of the ball is separated by an angle α0 from it. The situation of any other galaxy is characterized by an α1. The apparent distance between galaxies is equal
r = R (α0+ α1) (3)
where R - radius of our universe. In accordance with expression (2) the speed of one galaxy with respect to the other is
Vrel = V0 + V1 = c (sin α0 + sin α1). (4)
Represent the sine sum of the angles as follows:
sin (α0 + α1) = sin α0 cos α1 + sin α1 cos α0 = sin α0 + sin α1. (5)
The last equality is valid for small angles α0 and α1, or small compared to the speed of light values of the velocities V0 and V1. Comparing the last three expressions, we obtain
Vrel = c sin (r / R) ≈ c (r/R - 1/6 (r/R)3) (6)
In a first approximation, we have Hubble's law (1), where H = c / R. Substituting the last expression, the experimental value [4], the Hubble constant H = 2.3 10-18 s-1, we obtain an estimate of the radius of the Universe:
R = 1.3 1026 m = 0.137 1011 ly (7)
However, due to the nonlinearity of the dependence (6) the velocities of galaxies at large distances are inflated or otherwise, the values of the distances to galaxies too low for large values of velocities. This means that the radius of the universe is actually more obtained in (7).
Thus, the recession of galaxies is directly related to their creation, when the collision of our Universe with the flow of clots 4D-matter were formed at first holes (possibly cross-cutting) in the depths of the universe, which then collapsed due to (hyper-)surface tension gave rise to clusters of matter, smaller size and eventually become the galaxies. The immediate cause of their movement is the difference in effect of surface tension on the walls of the holes, passing obliquely with respect to the boundary of the Universe, to its border hypersurface. The increase in volume of the Universe does not happen in this process. It only may take place due to absorption of clusters that fall in the Universe, and the formation of stable holes or black holes. But the influence of these factors seem to be small and it can not be permanent. The merger is our Universe with another universe of approximately the same size, which would result in a significant change in volume, it is unlikely and if it happened it might have catastrophic consequences for the whole Universe
The fact that galaxies are spatially distributed fairly rare, said that the source gave rise to clots of 4D-matter located far away, and that the density of the universe in 4D-space is rather low
The knowlage of the velocity distribution of galaxies could help in determining the angle &alpha0;, or the velocity of our galaxy, the Milky Way, in the frame of reference associated with the medium, or by other words, in the absolute frame of reference - but only relatively to our Universe! As well as anomalies of the relic radiation, the nature of which, in our opinion, is related to the genesis of stellar objects by the method described above.
The latter observation [5] showed that the Universe has the region free from the galaxies. This fact is easily explained if we assume that in the path flow of aggregates of 4D-matter that has been bombed our Universe was another universe, which shield the area. Because the effect of "bounce", the secondary reflection clots from such a universe, galaxies may have formed from special values of velocities, which do not fit into a simple relationship (1). Of course, such a galaxy could arise due to the presence of other sources of clots.
As well the other conjecture can be proposed to explain the dark area. The clods of the "alien" 4D-matter fell on our Universe didn't come across it and we see there her pure hypersurface, the 4D-vacuum. Otherwise, in both cases we see nothing there.
[1] V. Skorobogatov. Light in the 4D-model of the ether. 2006. article2a.html.
[2] V. Skorobogatov. Some consequence 4D-model of the ether. 2006 article3a.html.
[3] V. Skorobogatov. Reference system in the 4D-model of the ether. 2007 article6a.html.
[4] Hubble's Law. 2007 Vikipedia
[5] Astronomers find gaping hole in the Universe. 2007. Physorg, Aug 23, 2007